I = ½ m (r 22 + r 12) I = (1/2) m ( r 1 2 + r 2 2 ) Web moment of inertia of a hollow cylinder that is rotating on an axis passing through the centre of the cylinder where it has an internal radius r 1 and external radius r 2 with mass m can be expressed in the following manner. Web if the xy plane is at the base of the cylinder, i.e. We can also use the moment of inertia for a hollow sphere ( 23ma2 2 3 m a 2 ) to calcul ate the moment of inertia of a nonuniform solid sphere in which the density varies as.
Web the moment of inertia of a hollow cylinder rotating about an axis passing through the centre of the cylinder can be determined by the given formula; Center, parallel to axis \(mr^2\) cylinder, solid: The formula for the moment of inertia for a hollow cylinder is: 1 the ratio of accelerations between these two objects is 4/3, which can be observed when rolling them simultaneously or via reasonably careful timing. Web for a solid cylinder, the moment of inertia, i, is known to be i = 1 / 2 mr 2, while a hollow cylinder has i = mr 2.
Jun 17, 2018 the answer is option(a), please see the explanation below. Web in this video we studied about the concept of moment of inertia of a hollow cylinder.you may download hand written rough pdf notes of rotational dynamics her. I = ½ m (r 22 + r 12) We can also use the moment of inertia for a hollow sphere ( 23ma2 2 3 m a 2 ) to calcul ate the moment of inertia of a nonuniform solid sphere in which the density varies as. I = (1/2) m ( r 1 2 + r 2 2 )
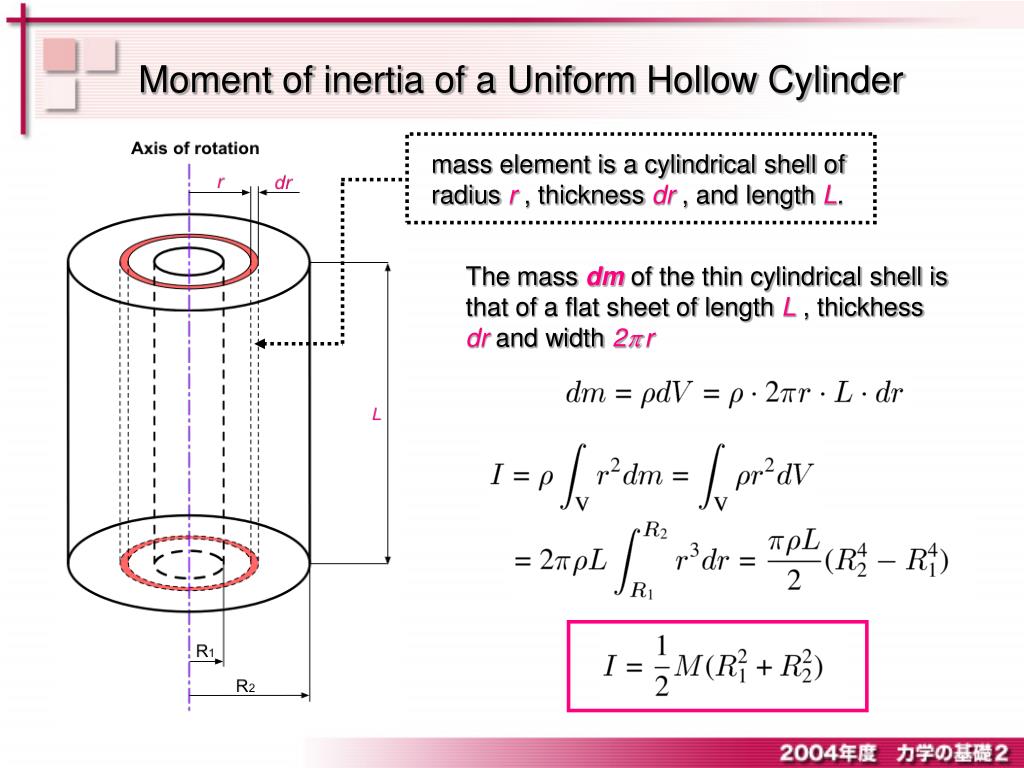
Web density = dm / dv where: Web this video uses the tools of calculus to derive the formula for the rotational inertia (moment of inertia) for a hollow cylinder. The expression for the moment of inertia of a hollow cylinder or hoop of finite thickness is obtained by the same process as that for a solid cylinder. As we know the moment of inertia is incomplete without the mass m so we will be using. M = mass of hollow cylinder;
Web this video uses the tools of calculus to derive the formula for the rotational inertia (moment of inertia) for a hollow cylinder. D o = cylinder outside diameter. Web for a solid cylinder, the moment of inertia, i, is known to be i = 1 / 2 mr 2, while a hollow cylinder has i = mr 2. I = 1/2 m ( ri 2 + ro 2) where.
Web Density = Dm / Dv Where:
D o = cylinder outside diameter. Web the moment of inertia of a hollow cylinder rotating about an axis passing through the centre of the cylinder can be determined by the given formula; The process involves adding up the moments of infinitesmally thin cylindrical shells. The moment of inertia is returned in kilogram⋅meters squared (kg·m²).
The Area Moment Of Inertia For A Hollow Cylindrical Section Can Be Calculated As.
I = 1/2 m ( ri 2 + ro 2) where. Newton's 2ⁿᵈ law relates force to acceleration. Web this college physics and calculus video tutorial explains how to derive the formula for the inertia of a hollow cylinder as well as a solid cylinder. As we know the moment of inertia is incomplete without the mass m so we will be using.
We Have We Can Obtain Moment Of Inertia By Integrating Over All These Hoops Cylinder Has Uniform Density, Where Þ = Constant Volume Of This Cylinder Is Mass M Is Since
I x = i y = 1 12 m ( 3 ( r 2 2 + r 1 2 ) + 4 h 2 ) {\displaystyle i_{x}=i_{y}={\frac {1}{12}}m\left(3\left(r_{2}^{2}+r_{1}^{2}\right)+4h^{2}\right)} Web moment of inertia (moi): Web hollow cylindrical cross section. We can also use the moment of inertia for a hollow sphere ( 23ma2 2 3 m a 2 ) to calcul ate the moment of inertia of a nonuniform solid sphere in which the density varies as.
Web A Hollow Cylinder With Rotating On An Axis That Goes Through The Center Of The Cylinder, With Mass M, Internal Radius R 1, And External Radius R 2, Has A Moment Of Inertia Determined By The Formula:
Center, parallel to axis \(mr^2\) cylinder, solid: Jun 17, 2018 the answer is option(a), please see the explanation below. Web in this video we studied about the concept of moment of inertia of a hollow cylinder.you may download hand written rough pdf notes of rotational dynamics her. Calculate the moment of inertia for uniformly shaped, rigid bodies apply the parallel axis theorem to find the moment of inertia about any axis parallel to one already known calculate the moment of inertia for compound objects
For this calculation, we will use an internal radius r 1 and external radius r 2. Web from newton’s 2ⁿᵈ law, f t = m a t. The moment of inertia is returned in kilogram⋅meters squared (kg·m²). R1 = distance between axis and inside of hollow cylinder This can also be written as f t = m ( r α).








Ads